Accounting for Governmental & Nonprofit Entities

Governmental financial statements provide a detailed overview of a government entity’s financial activities and position, serving as a tool for transparency and accountability. These statements are typically governed by the Governmental Accounting Standards Board (GASB), which establishes guidelines for state and local governments’ financial reporting. At their core, governmental financial statements are designed to provide stakeholders with a comprehensive picture of a government’s financial health, including its cash flows, assets, liabilities, and overall fiscal sustainability. This article explores the core aspects of governmental and nonprofit accounting, including fund accounting, budgetary control, revenue recognition, financial statements, grant management, cost allocation, and performance metrics. This classification system helps nonprofits manage donor expectations and ensures that funds are used according to donor intentions. It also provides stakeholders with a clear understanding of the organization’s financial health and resource allocation.
Choosing the Right Depreciation Method for Your Business Assets
The Statement of Functional Expenses, a key component of nonprofit financial reporting, further breaks down expenses by function, enhancing transparency and accountability. Modern financial management software like Workday Adaptive Planning and Oracle NetSuite offers robust functionalities for real-time data analysis and reporting. These platforms facilitate dynamic budgeting that can adapt to changing conditions, providing organizations with the agility needed to respond to unforeseen financial challenges.
Accounting for Governmental & Nonprofit Entities w/Connect 17th Edition
- It involves segregating resources into various funds, each with its own set of accounts, to ensure proper use and accountability.
- These organizations prioritize public service over profit, requiring specialized accounting practices to ensure transparency and accountability.
- Periodic audits verify compliance and identify discrepancies or potential areas for improvement, helping nonprofits maintain the trust of funding partners and secure continued financial support.
- Unlike for-profit entities, these organizations operate under financial principles tailored to their specific objectives and stakeholders.
- Fund accounting is central to financial management in governmental and nonprofit organizations, offering a structured method for tracking resources.
In addition to discussing strategic decisions facing API, the case covers performance measurement topics commonly integrated in managerial and cost accounting courses. API’s Board of Directors (BOD) must make important strategic planning and implementation decisions during a period of change. One Board member has suggested using performance measures to assess API’s progress in implementing strategy and achieving goals. Students are asked to develop financial and nonfinancial measures relevant to API’s strategy and to show how their suggested measures would appear in a balanced scorecard. Whether CPAs should be obligated to provide volunteer accounting for governmental & nonprofit entities accounting services to the community is another issue that the case requires students to address. A key component of these statements is the government-wide financial statement, which includes both the statement of net position and the statement of activities.
- For government entities, the Governmental Accounting Standards Board (GASB) is the authoritative body.
- Nonprofits often categorize funds as unrestricted, temporarily restricted, or permanently restricted, reflecting varying donor-imposed limitations.
- She joined the author team of Accounting for Governmental and Nonprofit Entities on the 16th edition.
- Professor Reck has received several research and teaching awards and has chaired or served on many doctoral dissertation committees.
- By implementing such technology, government and nonprofit entities can enhance transparency, accountability, and decision-making efficiency.
- She joined as an author for Accounting for Governmental & Nonprofit Entities on the 14th edition.
Homework Help by Business Subjects
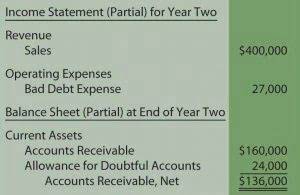
The primary components typically include the Statement of HOA Accounting Net Position, the Statement of Activities, and the Fund Financial Statements. One of the primary distinctions between government and nonprofit accounting lies in the governing bodies that set their respective financial reporting standards. Performance reporting assesses the effectiveness and efficiency of government programs and services. This helps improve service delivery and fosters accountability by providing evidence of resource allocation. For instance, a local government might track metrics like the cost per mile of road maintenance or the number of public safety incidents responded to within a specified time frame. Nonprofit organizations use net asset classification to manage and report their financial resources.
Nonprofits must also manage restricted funds, recording them separately from unrestricted funds to comply with donor intentions and enhance transparency. Software platforms like Sage Intacct and NetSuite Nonprofit Edition assist in managing these complexities, offering features for tracking and reporting restricted versus unrestricted funds. This method helps nonprofits manage their finances effectively by matching revenues with the period in which they are earned and related expenses are incurred.
ISE Accounting for Governmental & Nonprofit Entities Paperback – April 23, 2021

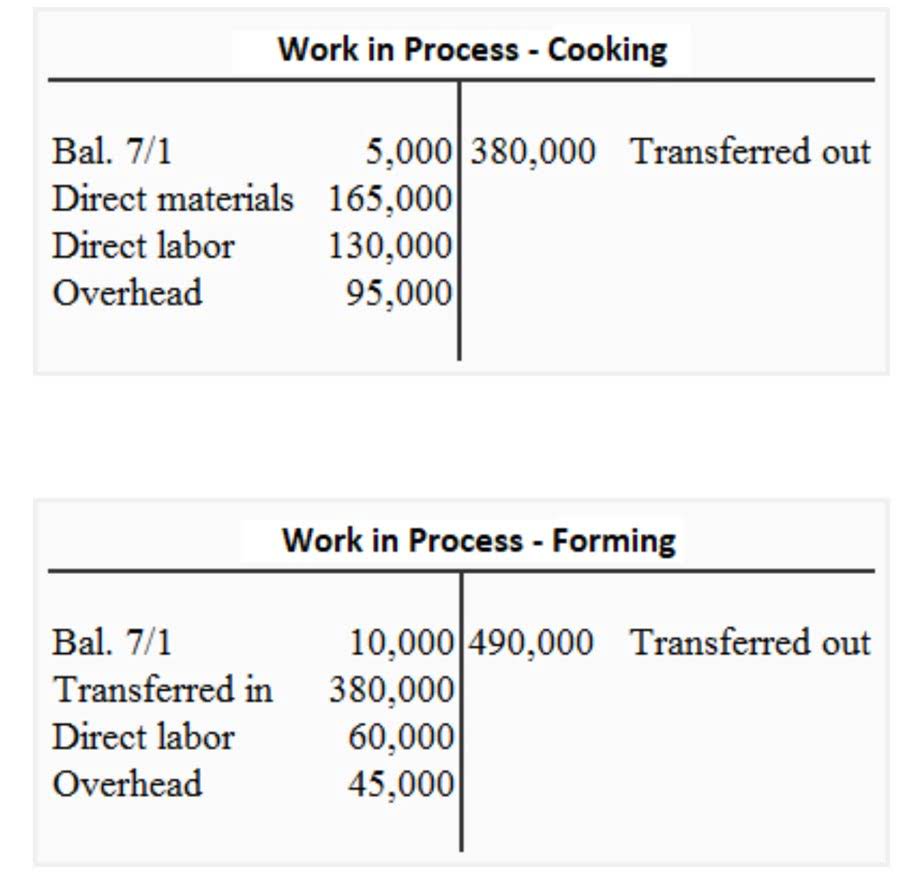
This involves forecasting revenues and expenses, considering historical data and future projections. Tools like Adaptive Insights and Workday Adaptive Planning facilitate this process, offering platforms for budget creation, analysis, and reporting. These tools provide real-time data analysis, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and adapt to changing circumstances. Double-entry bookkeeping is a key component of fund accounting, recording every transaction in at least two accounts to maintain the accounting equation’s balance. This system provides a comprehensive view of an organization’s financial position, aiding informed decision-making.
Accounting for Governmental & Nonprofit Entities: 2025 Release Kindle Edition
This budget must align with strategic goals and legislative mandates, necessitating an understanding of revenue projections and expenditure requirements. Governments often rely on historical data, economic forecasts, and policy priorities to craft a budget addressing immediate needs while safeguarding cash flow long-term fiscal health. Accounting for government and nonprofit entities presents unique challenges distinct from traditional business accounting. These organizations prioritize public service over profit, requiring specialized accounting practices to ensure transparency and accountability. We attempt to cover the basic accountingand financial reporting principles in as comprehensive a manner as possible. To keep the text practicaland “real world,” we enhanced the discussion of the principles with numerousillustrations drawn from financialreports prepared by actual governments and nonprofit organizations.
for Governmental and Nonprofit Organizations.
Finally, we designedthe end-of-chapter questions,exercises, problems,and cases specifically to help students better understand the material covered in our text. Navigating the complexities of revenue recognition in nonprofits requires understanding both accounting principles and the unique nature of nonprofit funding sources. Nonprofits often receive revenues from various sources, including donations, grants, membership fees, and program service fees.
0 comments