WORKER SAFETY

Potential hazards for workers at the site:
- Falls from heights & slip;
- Trench collapse;
- Scaffolding collapse;
- Electric shock and arc flash/arc blast;
- Failure to use personal protective equipment;
- Repetitive motion injuries.
SAFETY CHECKLIST
- EYE AND FACE PROTECTION
Safety glasses, selected based on anticipated hazards during welding, cutting, grinding and chemical applications.
- FOOT PROTECTION
Boots with safety-toed footwear slip-resistant and puncture-resistant soles.
- HAND PROTECTION
Snug fit gloves based on anticipated hazards during, welding, chemical application & electrical works.
- HEAD PROTECTION
Hard hats where there is a potential for objects falling from above, bumps to their heads from fixed objects & accidental head contact with electrical hazards.
- SCAFFOLDING & LADDERS
Must be erected on sound footing under supervision.
All scaffolds should be fully planked tightly.
Scaffolds must be at least 10 feet from electric power lines & heat source.
Scaffold must be equipped with guardrails, mid-rails and toe boards avoid makeshift extension on platforms to raise work height.
- ELECTRICAL SAFETY
Work on circuits is prohibited until all power is shut off and grounds are attached.
A useful Lockout/Tag-out system is in place.
Damaged electrical cords or cables are promptly replaced.
All extension cords have grounding prongs.
Three-wire portable electrical tools on extension cords.
Do not bypass any protective system or device.
Overhead electrical power lines are located and identified.
Ensure that ladders, scaffolds, equipment 10 feet away from power lines.
- FLOOR AND WALL OPENINGS
A secured cover, a guardrail guard openings.
Toeboards installed around the edges of permanent floor openings where persons may pass below the openings.
- ELEVATED SURFACES & STAIRWAYS
Signs are posted showing the elevated surface load capacity.
Surfaces elevated more than 48 inches above the floor or ground have standard guardrails.
All elevated surfaces where machines are placed have 4-inch toe boards.
Free of dangerous objects & debris.
Conditions must be corrected immediately.
- TRENCHES
Protective system to shore the trench.
Always provide a way to exit a trench, such as ladder, stairway or ramp make sure the trenches are reinspected after any hazard increasing event.
- HAZARD COMMUNICATION
A list of hazardous substances used in the workplace is maintained and readily available at the worksite (MSDS).
Train workers about the risk of each hazardous chemical being used.
Store safety
Provide personal protective equipment & enforce its use.
- CRANE SAFETY
Cranes and derricks are restricted from operating within 10 feet of any electrical power line.
The upper rotating structure supporting the boom and materials being handled is provided with an electrical ground while working near energized transmitter towers.
Rated load capacities, operating speed and instructions are posted and visible to the operator.
Cranes are equipped with a load chart.
The operator understands and uses the load chart.
The operator can determine the angle and length of the crane boom at all times.
Crane machinery and other rigging equipment is inspected daily prior to use to make sure that it is in good condition.
Accessible areas within the crane’s swing radius are barricaded.
Tag lines are used to prevent dangerous swing or spin of materials when raised or lowered by a crane or derrick.
Illustrations of hand signals to crane and derrick operators are posted on the job site.
The signal person uses correct signals for the crane operator to follow.
Crane outriggers are extended when required.
Crane platforms and walkways have antiskid surfaces.
Broken, worn or damaged wire rope is removed from service.
Guardrails, hand holds and steps are provided for safe and easy access to and from all areas of the crane.
Load testing reports/certifications are available.
Tower crane mast bolts are properly torqued to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Overload limits are tested and correctly set.
The maximum acceptable load and the last test results are posted on the crane.
Initial and annual inspections of all hoisting and rigging equipment are performed and reports are maintained.
Only properly trained and qualified operators are allowed to work with hoisting and rigging equipment.
- FORKLIFTS
Forklift truck operators are competent to operate these vehicles safely as demonstrated by their successful completion of training and evaluation.
No employee under 18 years old is allowed to operate a forklift.
Forklifts are inspected daily for proper condition of brakes, horns, steering, forks and tires.
Powered industrial trucks (forklifts) meet the design and construction requirements established in American National Standards Institute (ANSI) for Powered Industrial Trucks, Part II ANSI B56.1-1969.
Written approval from the truck manufacturer is obtained for any modification or additions which affect capacity and safe operation of the vehicle.
Capacity, operation and maintenance instruction plates, tags or decals are changed to indicate any modifications or additions to the vehicle.
Battery charging is conducted in areas specifically designated for that purpose.
Material handling equipment is provided for handling batteries, including conveyors, overhead hoists or equivalent devices.
Reinstalled batteries are properly positioned and secured in the truck.
Smoking is prohibited in battery charging areas.
Precautions are taken to prevent open flames, sparks or electric arcs in battery charging areas.
Refresher training is provided and an evaluation is conducted whenever a forklift operator has been observed operating the vehicle in an unsafe manner and when an operator is assigned to drive a different type of truck.
Load and forks are fully lowered, controls neutralized, power shut off and brakes set when a powered industrial truck is left unattended.
There is sufficient headroom for the forklift and operator under overhead installations, lights, pipes, sprinkler systems, etc.
Overhead guards are in place to protect the operator against falling objects.
Trucks are operated at a safe speed.
All loads are kept stable, safely arranged and fit within the rated capacity of the truck.
Unsafe and defective trucks are removed from service.
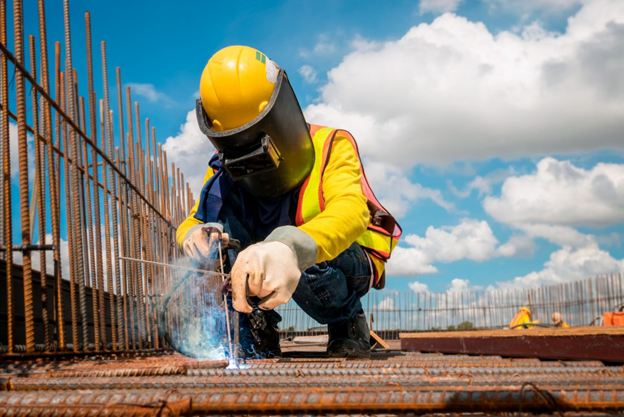

All of the above mentioned precautions can not be ignored and must be taken under consideration.
0 comments